Understanding 3D spaces has long been a challenge for artificial intelligence, bridging the gap between digital perception and human-like comprehension. GPT4Scene, a cutting-edge framework, redefines this challenge by using only vision inputs to navigate complex 3D environments. Unlike traditional approaches that rely on point clouds or intricate multi-modal datasets, GPT4Scene adopts a purely vision-based approach inspired by human perception. By constructing a Bird’s Eye View (BEV) image and integrating spatial-temporal markers, this framework enhances Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to achieve state-of-the-art performance. As embodied AI applications in robotics, smart homes, and industrial inspections proliferate, GPT4Scene promises to be a cornerstone for advancing 3D scene understanding.
How Vision-Based Models Reshape 3D Scene Understanding
The Challenge of 3D Comprehension
Traditional 3D scene understanding methods rely heavily on point clouds and multi-modal inputs. While these approaches excel in detail capture, they often fall short in aligning global and local information — a critical factor for holistic scene comprehension. Additionally, point clouds lack nuanced textures and materials, leaving gaps in their spatial representation. GPT4Scene challenges this paradigm by leveraging vision inputs — video frames processed into panoramic BEV images — to contextualize scenes comprehensively.
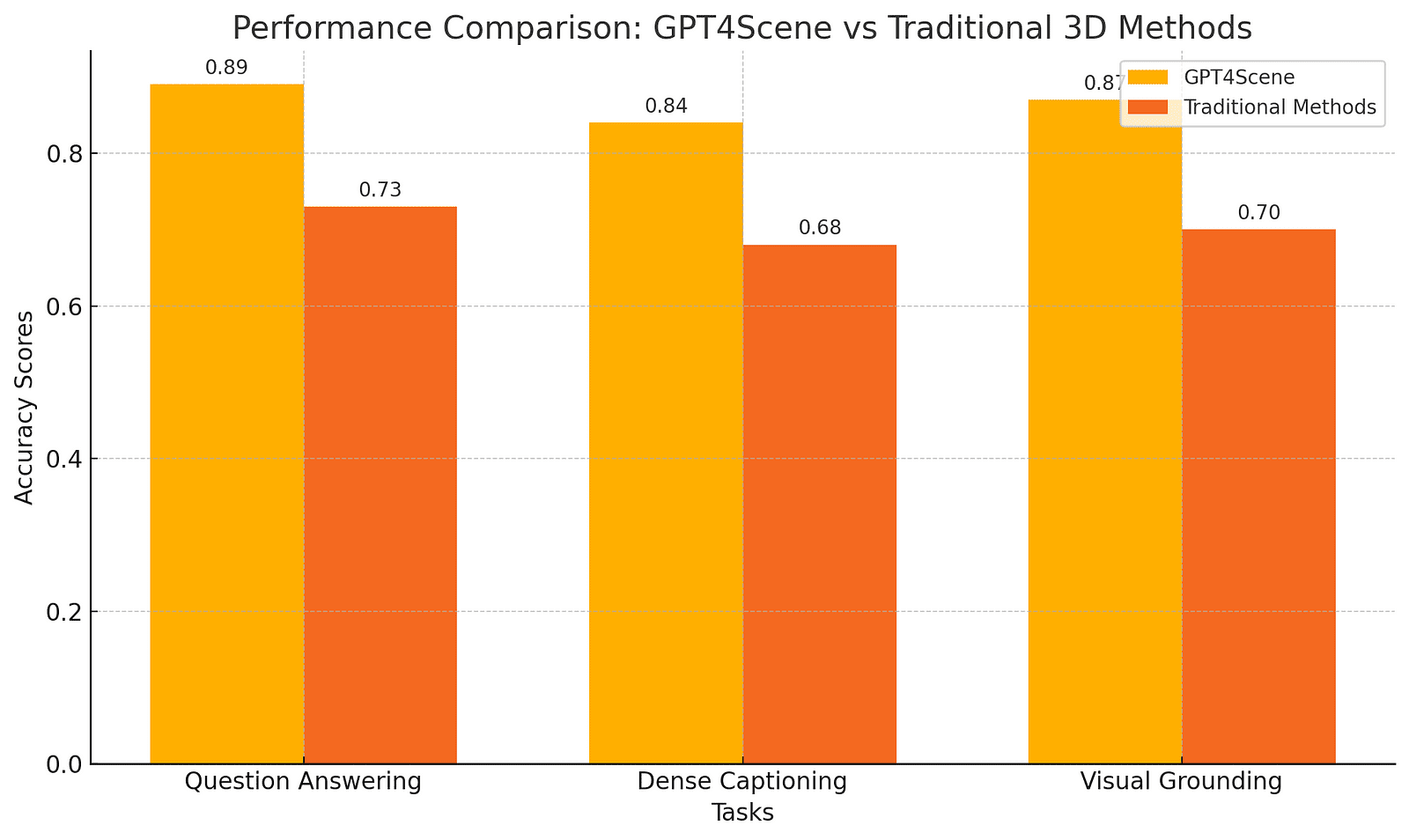
A comparison chart below illustrates the performance differences between traditional 3D point cloud methods and GPT4Scene in various tasks like question answering and dense captioning.
The Role of BEV and STO Markers
GPT4Scene introduces a novel technique: generating BEV images from video inputs and embedding Spatial-Temporal Object (STO) markers. These markers maintain consistency across video frames and the BEV map, enabling seamless integration of local and global information. By labeling objects in the scene, GPT4Scene empowers VLMs to link object identities to spatial contexts. For instance, identifying a chair’s precise position relative to a table becomes intuitive for the model, even in cluttered environments.
Real-World Implications
Applications for this breakthrough extend to various domains. In industrial inspections, GPT4Scene aids in identifying anomalies in machinery by mapping their locations and understanding spatial arrangements. Smart home technologies benefit from enhanced navigation and interaction capabilities, enabling robots to navigate seamlessly. Moreover, the integration of BEV and STO markers has proven invaluable for embodied AI tasks, such as multi-turn dialogues or spatial reasoning.
Advancements in Fine-Tuning Vision-Language Models
The ScanAlign Dataset
To optimize open-source VLMs, the creators of GPT4Scene developed ScanAlign, a dataset containing 165,000 annotations derived from RGB-D indoor scans. This dataset pairs video frames, BEV images, and STO markers with rich text annotations, enabling fine-tuning that bridges the gap between raw inputs and actionable insights. Unlike previous datasets that prioritize single-task performance, ScanAlign is versatile, supporting question answering, dense captioning, and visual grounding tasks.
Fine-Tuning vs. Zero-Shot Performance
While GPT4Scene achieves remarkable results in zero-shot settings with closed-source VLMs like GPT-4o, the fine-tuned models exhibit transformative performance gains. Metrics such as BLEU and CIDEr scores improve significantly, showcasing the synergy between tailored datasets and advanced frameworks. For example, Qwen2-VL-7B’s BLEU-1 score rose by 56% after fine-tuning with ScanAlign, underlining the dataset’s effectiveness in enhancing spatial reasoning capabilities.
How Machines Learn to Map 3D Spaces
GPT4Scene’s BEV maps condense panoramic spatial data into accessible formats, allowing VLMs to “see” entire scenes from above.
The Power of STO Markers
By maintaining temporal and spatial consistency, STO markers ensure object identities remain coherent across multiple frames.
State-of-the-Art Results
GPT4Scene fine-tuned models outperform traditional 3D approaches by up to 40% in accuracy across benchmarks like ScanRefer and Multi3DRef.
Vision-Based Simplicity
Unlike multi-modal systems, GPT4Scene uses pure video inputs, mirroring human reliance on visual cues.
Enabling Embodied Intelligence
The framework’s intuitive understanding of 3D spaces is paving the way for smarter robots and virtual assistants.
The Path Forward: Vision-Based Intelligence
The rise of GPT4Scene signals a shift in how AI perceives and interacts with 3D spaces. Its vision-first approach not only simplifies data requirements but also amplifies performance across diverse tasks. By aligning local object details with global scene layouts, GPT4Scene bridges a crucial gap in embodied AI. As datasets like ScanAlign continue to refine these capabilities, the future of 3D scene understanding looks promising. With smarter, more intuitive models, we stand on the cusp of a technological revolution that could redefine our relationship with AI.
About Disruptive Concepts
Welcome to @Disruptive Concepts — your crystal ball into the future of technology. 🚀 Subscribe for new insight videos every Saturday!
See us on https://twitter.com/DisruptConcept
Read us on https://medium.com/@disruptiveconcepts
Enjoy us at https://disruptive-concepts.com
Whitepapers for you at: https://disruptiveconcepts.gumroad.com/l/emjml
New Apps: https://2025disruptive.netlify.app/







