
Imagine gazing into the farthest reaches of space, where quasars — the universe’s most luminous objects — reside. These celestial giants are not just bright; they’re puzzling, especially when observed at high redshifts, meaning they’re seen as they existed billions of years ago. High-redshift quasars challenge our understanding of how massive black holes form and grow because they seem to have achieved impossible masses in a fraction of the cosmic timeline. Such observations suggest black holes with masses billions of times that of our Sun, begging the question: how did they grow so massive so quickly?
Understanding Quasar Luminosity
To grasp why these high-redshift quasars are so perplexing, we must first understand the concept of luminosity and its deceptive nature. Quasars emit an incredible amount of light, traditionally thought to correlate directly with the mass of their central black holes. The more massive the black hole, the greater the gravitational pull, allowing it to accrete more material and emit more energy. However, recent insights suggest that this luminosity might not be as straightforward as it seems. It may involve beaming — a process where light is emitted in a specific direction, making the quasar appear brighter than it actually is without needing a supermassive black hole.
To better understand the difference between beamed and normal quasars, here’s a graph below that compares their apparent luminosity, actual mass, and distance from us:
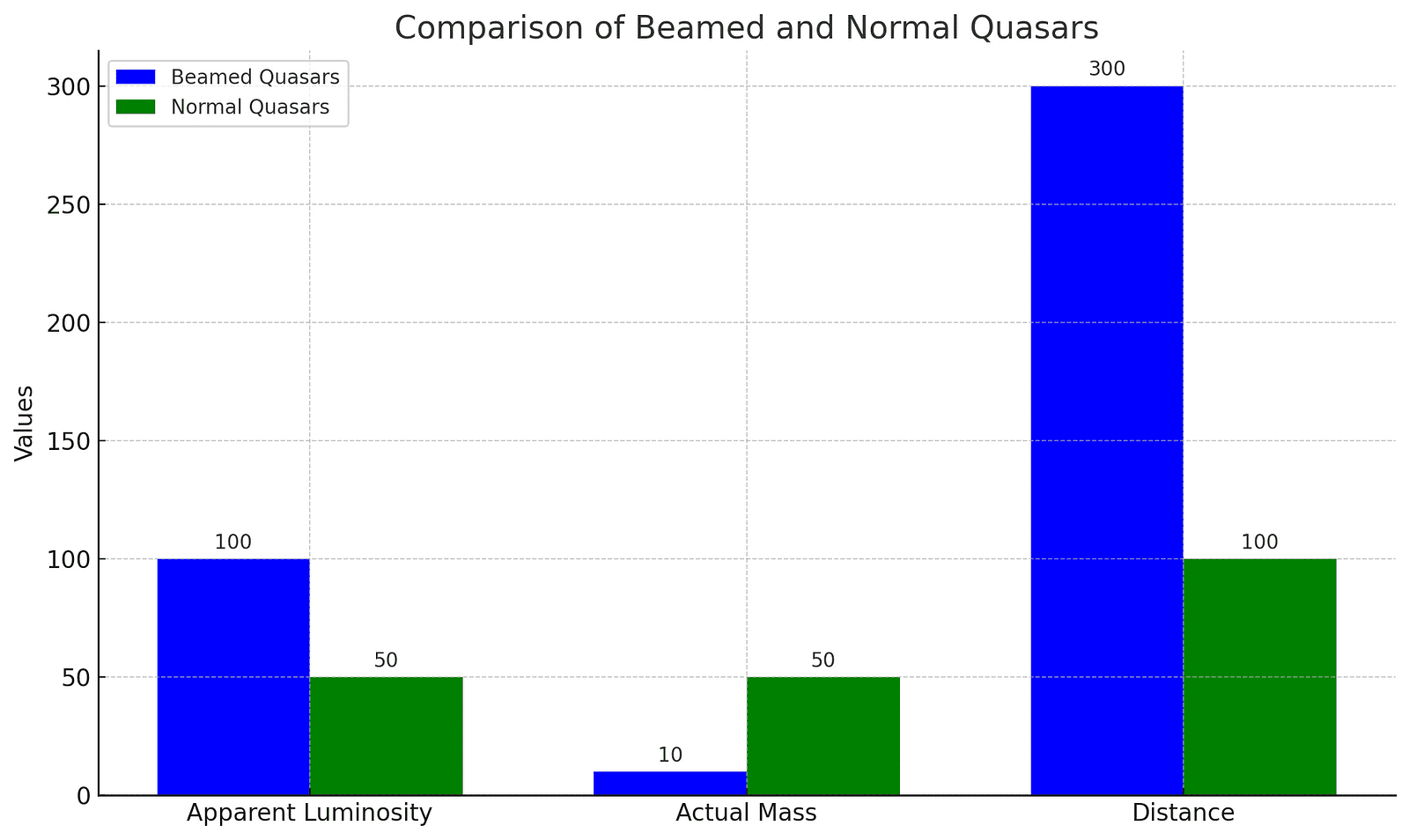
Rethinking Black Hole Mass Estimates
The traditional method of estimating black hole masses through the light they emit might lead us astray. The beaming effect, akin to a lighthouse beam, means we might only see a concentrated burst of light when we’re in the direct path of the beam, falsely inflating our estimates of the black hole’s size. This revelation comes from studying similar effects in ultraluminous X-ray sources, smaller systems that appear incredibly bright due to the same deceptive beaming. This analogy suggests that many quasars might actually harbor black holes with much smaller masses, challenging the prevailing theories of their rapid growth.
Implications of Misjudged Luminosity
The implications of misjudged quasar luminosity extend beyond academic curiosity; they reshape our understanding of the universe’s evolution. If high-redshift quasars are not as massive as previously thought, then our theories on the formation of cosmic structures, the role of black holes in galaxy evolution, and the dynamics of early universe matter distribution must be reconsidered. This could mean that black holes, and by extension galaxies, grow and evolve in ways that are significantly different from our current models, possibly involving more ordinary processes and common events rather than requiring extraordinary circumstances.
Towards a New Understanding of Quasars
As we delve deeper into the study of quasars and the mysteries of their luminosity, we edge closer to a more nuanced understanding of the universe. Upcoming technologies and telescopes might soon provide the tools needed to test these theories, potentially confirming or refuting the beaming model and helping us refine our models of how the universe’s most massive objects form and influence their surroundings. The journey to understand quasars not only satisfies our curiosity but also enhances our understanding of fundamental physics and the universe’s grand narrative.
Record Breakers
Quasars are the most distant objects visible to astronomers, shining a light on the universe’s early days. Their brightness allows us to study them even when they are billions of light-years away.
Powerhouses
A single quasar can outshine an entire galaxy of billions of stars, with some emitting more energy than 1,000 Milky Way galaxies combined.
Cosmic Engines
At the heart of every quasar is a supermassive black hole, some with masses exceeding a billion suns. These black holes power the quasar’s incredible luminosity.
Builders of the Universe
Quasars play a critical role in galaxy formation and evolution, with their immense energy and matter outflows influencing star formation and the intergalactic medium.
Time Capsules
By studying quasars, astronomers can unravel the conditions of the early universe, providing clues about its expansion rate, the formation of structures, and the nature of dark matter.
Inspiring Future Explorers
Quasars are not just astronomical phenomena; they are beacons in the vast cosmos that guide our understanding of the universe. Each discovery about their nature challenges old views and provides fresh insights into the fundamental forces shaping everything from galaxies to the vast stretches of the cosmic web. For people fascinated by the mysteries of space, quasars offer a compelling glimpse into high-energy physics, cosmology, and the endless possibilities of discovery. As we stand on the brink of new astronomical technologies, the next generation of scientists could be the ones to unlock the secrets of these cosmic giants, perhaps revealing more about our universe than we ever imagined possible. This journey of discovery isn’t just about answering questions but about inspiring a lifelong quest for knowledge and understanding in the hearts of explorers everywhere.
About Disruptive Concepts
https://www.disruptive-concepts.com/
Welcome to @Disruptive Concepts — your crystal ball into the future of technology. 🚀 Subscribe for new insight videos every Saturday!







