
Ever heard of the term “Old Man Aldehyde”? It’s a nickname given lovingly to a specific chemical that’s responsible for the distinct smell often associated with older people. This article delves into what causes this unique scent and why it’s a normal part of aging.
What is ‘Old Man Aldehyde’?
‘Old Man Aldehyde’ refers to nonenal, an organic compound that starts appearing in greater quantities as people age. Nonenal is an unsaturated aldehyde. To understand this better:
- Unsaturated: This means there are double bonds between some of the carbon atoms in the molecule.
- Aldehyde: A type of chemical compound with a specific structure that influences its reactions.
Nonenal is produced when omega-7 unsaturated fatty acids on the skin degrade over time. This process is accelerated in older adults due to changes in the skin and body chemistry.
Why Do Older People Produce More Nonenal?
As we age, our skin changes significantly. It becomes thinner, less elastic, and the oils it produces alter in composition. These changes contribute to the production of more nonenal.
Hormonal Shifts
Hormones greatly influence our body’s chemistry. With age, hormonal changes affect the skin’s oil production, leading to an increase in nonenal.
Younger People vs. Older People
Younger individuals also have nonenal, but their bodies produce it in much lower quantities. This is due to higher levels of antioxidants in younger skin, which combat the degradation of fatty acids.
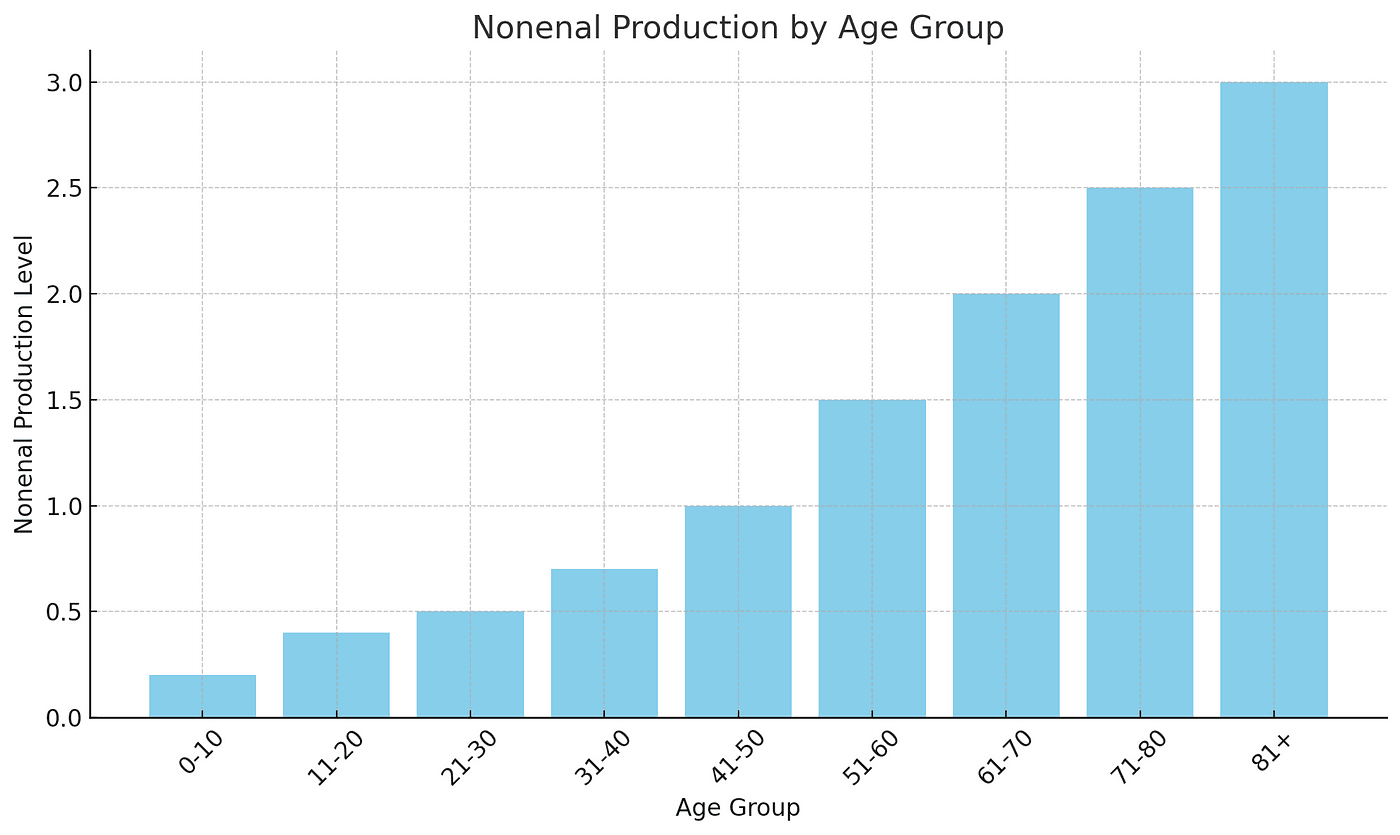
To further explain the concept of nonenal production and its relation to age, we can refer to the graph above. This graph visually represents how nonenal production varies across different age groups. As you can see, the level of nonenal production generally increases with age.
How People Perceive ‘Old Man Aldehyde’
The reaction to the smell of nonenal varies. Some might find it noticeable and distinct, while others might not perceive it as strongly.
Cultural Context
Different cultures have different attitudes towards this smell. In some, it’s associated with experience and wisdom, while in others, it might not be as positively viewed.
Hygiene and Skin Care
Good hygiene and proper skin care can help manage nonenal production. Using mild soaps and moisturizers can keep the skin healthy while minimizing the scent.
Diet and Antioxidants
A diet rich in antioxidants might help reduce nonenal production by tackling the free radicals that break down fatty acids in the skin.
Fabric Care
As nonenal can stick to clothing, regular washing and the use of fabric conditioners can help reduce its presence on fabrics.
Worldwide Variance in Nonenal Production
The production of nonenal varies greatly around the world, which is fascinating. This variation can be attributed to genetic differences and dietary habits across different cultures. For instance, diets rich in certain types of fatty acids might lead to higher nonenal production. Furthermore, genetics play a crucial role in how our bodies metabolize these acids. This global variance not only highlights the diversity of the human species but also underscores the complex interplay between our genetics, environment, and diet in determining our body chemistry. Understanding these variations can provide valuable insights into managing aging-related changes more effectively across different populations.
Nonenal in Animals
Interestingly, humans are not the only ones who produce compounds like nonenal as they age. Many animals also produce similar chemicals. However, due to their different grooming habits and the way their senses are attuned, these scents are less noticeable in the animal kingdom. This similarity suggests a common biochemical process across different species related to aging. In studying these processes, scientists can gain a better understanding of aging, not just in humans but in the animal kingdom as well, potentially leading to broader insights into the biology of aging.
Historical Importance of Aging Scents
Throughout history, the distinct scents associated with aging have played an interesting role in some cultures. In certain societies, these smells were used to signify age and wisdom, often leading to greater respect for the elderly. This historical perspective shows how different cultures have understood and valued the aging process. It also reflects how sensory experiences, such as smell, can influence social structures and norms. These historical uses of aging scents offer a fascinating glimpse into how humans have historically interpreted and valued the natural signs of aging.
Changes in Skin pH with Age
As we age, the pH level of our skin undergoes significant changes, becoming more neutral compared to the more acidic skin of younger individuals. This shift in pH affects the skin’s microbiome — the collection of microorganisms living on our skin. Younger skin’s acidic environment supports certain types of bacteria, while the more neutral pH of older skin may encourage different types. These pH changes can influence not just the production of nonenal but also the overall health and appearance of the skin. Understanding these pH changes is crucial for developing age-appropriate skincare routines and products.
Research in Cosmetics for Nonenal
The increase in nonenal production with age has sparked significant interest in the cosmetic and healthcare industries. Researchers are actively exploring ways to reduce or neutralize this compound to address the concerns of an aging population. This research has led to the development of specialized products, including soaps and lotions, formulated to tackle the unique challenges of aging skin. These advancements not only improve the quality of life for older adults but also demonstrate the potential for science to provide solutions to the natural challenges of aging.
Nonenal and Health Indications
While nonenal itself is harmless, its increased presence is a telltale sign of aging skin, which may require different care than younger skin. Older skin tends to be drier and more fragile, making it more susceptible to damage and irritation. The rise in nonenal production can serve as a reminder to pay closer attention to skin health as we age. This includes using gentler products, staying hydrated, and possibly incorporating more antioxidants into our diet to combat the effects of aging.
Detection Thresholds of Nonenal
The ability to detect nonenal varies significantly among individuals. Some people can sense its presence at much lower concentrations, which may make them more sensitive to the so-called ‘elderly smell’. This variation in detection thresholds is not just a trivial fact; it has implications for how we perceive and interact with older adults. It also raises interesting questions about our sense of smell and how personal and environmental factors can influence it. Understanding these differences can lead to more empathetic and informed interactions across generations.
The Role of Antioxidants in Combating Nonenal
Antioxidants play a vital role in our skin’s health, particularly in combating the oxidative processes that lead to nonenal production. As we age, the natural antioxidant levels in our skin decrease, making us more susceptible to oxidative stress and the resulting increase in nonenal. By incorporating antioxidant-rich foods into our diet and using skincare products with antioxidants, we can help mitigate some of these aging effects. This underscores the importance of a holistic approach to health and wellness, especially as we age, where diet, skincare, and lifestyle choices all contribute to our overall well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding the chemistry behind ‘Old Man Aldehyde’ helps us appreciate the natural process of aging. Nonenal, the chemical behind this unique smell, is a normal part of growing older. By learning about it, we can approach aging with more empathy and understanding, recognizing that it’s a journey we all share.
About Disruptive Concepts
Welcome to @Disruptive Concepts — your crystal ball into the future of technology. 🚀 Subscribe for new insight videos every Saturday!







